Planning worship?
Check out our sister site, ZeteoSearch.org,
for 20+ additional resources related to your search.
- |
User Links
Person Results
‹ Return to hymnal

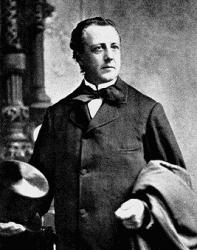








Export as CSV
James McGranahan

1840 - 1907 Hymnal Number: 590 Composer of "EL NATHAN" in Voices Together James McGranahan USA 1840-1907. Born at West Fallowfield, PA, uncle of Hugh McGranahan, and son of a farmer, he farmed during boyhood. Due to his love of music his father let him attend singing school, where he learned to play the bass viol. At age 19 he organized his first singing class and soon became a popular teacher in his area of the state. He became a noted musician and hymns composer. His father was reluctant to let him pursue this career, but he soon made enough money doing it that he was able to hire a replacement farmhand to help his father while he studied music. His father, a wise man, soon realized how his son was being used by God to win souls through his music. He entered the Normal Music School at Genesco, NY, under William B Bradbury in 1861-62. He met Miss Addie Vickery there. They married in 1863, and were very close to each other their whole marriage, but had no children. She was also a musician and hymnwriter in her own right. For a time he held a postmaster’s job in Rome, PA. In 1875 he worked for three years as a teacher and director at Dr. Root’s Normal Music Institute. He because well-known and successful as a result, and his work attracted much attention. He had a rare tenor voice, and was told he should train for the operatic stage. It was a dazzling prospect, but his friend, Philip Bliss, who had given his wondrous voice to the service of song for Christ for more than a decade, urged him to do the same. Preparing to go on a Christmas vacation with his wife, Bliss wrote McGranahan a letter about it, which McGranahan discussed with his friend Major Whittle. Those two met in person for the first time at Ashtubula, OH, both trying to retrieve the bodies of the Bliss’s, who died in a bridge-failed train wreck. Whittle thought upon meeting McGranahan, that here is the man Bliss has chosen to replace him in evangelism. The men returned to Chicago together and prayed about the matter. McGranahan gave up his post office job and the world gained a sweet gospel singer/composer as a result. McGranahan and his wife, and Major Whittle worked together for 11 years evangelizing in the U.S., Great Britain, and Ireland. They made two visits to the United Kingdom, in 1880 and 1883, the latter associated with Dwight Moody and Ira Sankey evangelistic work. McGranahan pioneered use of the male choir in gospel song. While holding meetings in Worcester, MA, he found himself with a choir of only male voices. Resourcefully, he quickly adapted the music to those voices and continued with the meetings. The music was powerful and started what is known as male choir and quartet music. Music he published included: “The choice”, “Harvest of song”, “Gospel Choir”,, “Gospel hymns #3,#4, #5, #6” (with Sankey and Stebbins), “Songs of the gospel”, and “Male chorus book”. The latter three were issued in England. In 1887 McGranahan’s health compelled him to give up active work in evangelism. He then built a beautiful home, Maplehurst, among friends at Kinsman, OH, and settled down to the composition of music, which would become an extension of his evangelistic work. Though his health limited his hours, of productivity, some of his best hymns were written during these days. McGranahan was a most lovable, gentle, modest, unassuming, gentleman, and a refined and cultured Christian. He loved good fellowship, and often treated guests to the most delightful social feast. He died of diabetes at Kinsman, OH, and went home to be with his Savior.
John Perry
James McGranahan
Charles C. Converse
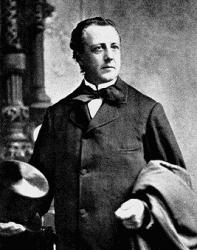
1832 - 1918 Hymnal Number: 628 Composer of "CONVERSE" in Voices Together Pseudonyms: Clare, Lester Vesé, Nevers, Karl Reden, Revons
=================================
Charles Crozat Converse LLD USA 1832-1918. Born in Warren, MA, he went to Leipzig, Germany to study law and philosophy, as well as music theory and composition under Moritz Hauptmann, Friedrich Richter, and Louis Plaidy at the Leipzig Conservatory. He also met Franz Liszt and Louis Spohr. He became an author, composer, arranger and editor. He returned to the states in 1859 and graduated from the Albany, NY, Law School two years later. He married Lida Lewis. From 1875 he practiced law in Erie, PA, and also was put in charge of the Burdetta Organ Company. He composed hymn tunes and other works. He was offered a DM degree for his Psalm 126 cantata, but he declined the offer. In 1895 Rutherford College honored him with a LLD degree. He spent his last years in Highwood, NJ, where he died. He published “New method for the guitar”, “Musical bouquet”, “The 126th Psalm”, “Sweet singer”, “Church singer”, “Sayings of Sages” between 1855 and 1863. he also wrote the “Turkish battle polka” and “Rock beside the sea” ballad, and “The anthem book of the Episcopal Methodist Church”.
John Perry
Charles C. Converse
César Malan

1787 - 1864 Person Name: Henri Abraham César Malan Hymnal Number: 759 Composer of "HENDON" in Voices Together Rv Henri Abraham Cesar Malan, 1787-1864. Born in Geneva, Switzerland, into a bourgeois family that moved to Switzerland to escape religious persecution during the French Revolution, he attended the university in Marseilles, France, intending to become a businessman. Although having some grounding in religious faith by his mother, he decided to attend the Academy at Geneva (founded by Calvin) in preparation for ministry. He was ordained in 1810, after being appointed a college master (teaching Latin) in 1809. Malan was in accord with the National Church of Geneva as a Unitarian, but the Reveil Movement caused him to become a dissident (evangelical) instead of a proponent of the Reformed Church (believing works, not faith, was what mattered). In 1811 he married (wife’s name not found). They had at least two children (one son was Solomon, referenced below). From 1813 on Malan slowly became an evangelical, after being given an understanding of true salvation through grace (not works) in 1816 by two German Lutherans from Geneva. He became saved upon this realization and was so changed that he burned his prized collection of classical authors and manuscripts. In 1817 he preached around Geneva, and one sermon in particular, “Man only justified by faith alone” created a firestorm and brought him into conflict with religious authorities of the region. From then on he wished to help reform the national church from within, but the forces of the Venerable Company were too strong for him and excluded him from the pulpits and caused his dismissal from his regentsship at the college in 1818. Others in agreement with Malan were Charles Spurgeon, Robert Wilcox, Robert Haldane, and Henry Drummond. In 1820 he built a chapel in his garden and obtained the license of the State for it as a separatist place of worship. He preached in that chapel 43 years. In 1823 he was formally deprived of his status as a minister of the national Church. Various events caused his congregation to diminish over the next few years, and he began long tours of evangelization subsidized by religious friends in his land, Belgium, France, England and Scotland. He often preached to large congregations. Malan also authorized a hymn book, “Chants de Sion” (1841). A strong Calvinist, Malan lost no opportunity to evangelize. On one occasion an old man he visited pulled Malan’s hymnal out and told him he had prayed to see the author of it before he died. On a visit to England Malan also inspired author, Charlotte Elliott, to write the hymn lyrics for “Just as I am”, when seeking an answer to her conversion she asked and he advised her to come to Christ ‘just as she was’. Malan published a score of books and also produced many religious tracts and pamphlets largely on questions in dispute between the National and evangelical churches of Rome. He also wrote articles in the “Record” and in American reviews. His hymns were set to his own melodies. He was an artist, a mechanic, a carpenter, a metal forger, and a printer. He had his own workshop, forge and printing press. One of his greatest joys was the meeting of the evangelical alliance at Geneva in 1861 which helped change church views. He retired to his home, Vandoeuvres, in the countryside near Geneva in 1857, dying there seven years later.. He was honored by a visit from the Queen of Holland two years before his death. He is mainly remembered as a hymn writer, having written 1000+ hymn lyrics and tunes. One son, Solomon, a gifted linguist and theologian, became Vicar of Broadwindsor. About a dozen of his hymns appeared translated in the publication “Friendly visitor” (1826). He was an author, creator, composer, editor, correspondent, contributor, translator, owner, and performer.
John Perry
=================
Malan, Henri Abraham César. The family of Malan traces its origin to the valleys of Piedmont. A branch of it settled at Mérindol, in Dauphiné, but was driven from France by the persecutions that followed the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. Pierre Malan [Cesar's father], after seeing his sister fall a victim to persecution, left Mérindol (1714), and arrived at Geneva (1722). Henri Abraham César Malan was born at Geneva in 1787. After an education at the College, he went to Marseilles, with the intention of learning business: but, soon after, entered the Academy at Geneva, as a preparation for the ministry, to which he was ordained in 1810. He had been appointed one of the masters at the College in the previous year. The National Church of Geneva was at that time almost Unitarian, and Malan's convictions were in accord with it. But the great movement known as the Réveil, of which the first products were the dissident church of Bourg de Four and at a later date that founded by Malan himself, and which finally imbued the whole Swiss Church with its spirit, was silently preparing itself. The germ of the movement may be traced in the Société des Amis (1810), of which Empeytaz and A. Bost were leaders; and in Malan's independent attainment to the doctrines of the Divinity of the Saviour and the free gifts of salvation through Him (1816). But the human agency, which gave it force, and determined its Calvinistic direction, was the visit of Robert Haldane (in the autumn of 1816), to whom not only these pioneers of the movement, but F. Monod, E. Rieu, Guers, Gonthier, Merle d'Aubigné, and others, always pointed as their spiritual father. Empeytaz and others sought to attain enfranchisement by the establishment of the "petite Eglise of Bourg de Four." Malan wished to reform the national Church from within: and a sermon at Geneva, which brought on him the obloquy of the professors and theologians that composed his audience, and which Haldane characterized as a republication of the Gospel, was his first overt act (Jan. 19, 1817). But the opposing forces were far too strong for him. The Venerable Company excluded him from the pulpits, and achieved his dismissal from his regentship at the College (1818). In 1820 he built a chapel (Chapelle du Temoignage) in his garden, and obtained the licence of the State for it, as a separatist place of worship. In 1823 he was formally deprived of his status as a minister of the national Church. The seven years that succeeded were the palmy days of the little chapel. Strangers, especially from England, mingled with the overflowing Swiss congregation. But (in 1830) a secession to Bourg de Four, and then the foundation of the Oratoire and the Société Evangelique, which in 1849 absorbed the congregation of Bourg de Four under the title of the Église Evangélique, thinned more and more the number of his adherents. His burning zeal for the conversion of souls found a larger outlet in long tours of evangelization, subsidized by religious friends, in his own land and Belgium and France, and also in Scotland and England, where he had friends among many religious bodies, and where he preached to large congregations. The distinguishing characteristic of these tours was his dealing with individuals. On the steamboat or the diligence, in the mountain walk, at the hotel, no opportunity was lost. On one occasion an old,man whom he visited drew from under his pillow a copy of his great hymnbook, Chants de Sion, 1841, and told him how he had prayed to see the author of it before he died.
It is as the originator of the modern hymn movement in the French Reformed Church that Malan's fame cannot perish. The spirit of his hymns is perpetuated in the analysis of Christian experience, the never-wearied delineation of the hopes and fears, the joys and sorrows of the believer's soul, which are still the staple of French Protestant hymns. To this was added, in Malan himself, a marked didactic tone, necessitated by the great struggle of the Réveil for Evangelical doctrine; and an emphatic Calvinism, expressing itself with all the despondency of Newton and Cowper, but, in contrast with them, in bright assurance, peace and gladness. French criticism has pronounced his hymns unequal, and full of literary defects; but their unaffected freshness and fervent sincerity are universally allowed. In the Chants de Sion, hymns 20, ”Hosanna! Béni soit"; 165, “Mon coeur joyeux, plein d'espérance"; 199, "Du Rocher de Jacob"; 200, "Agneau de Dieu"; 239, "Trois fois Jehovah," are in every Protestant French hymnbook; and several others are very widely used.
Besides his hymns Malan produced numberless tracts and pamphlets on the questions in dispute between the National and Evangelical Churches and the Church of Rome, as well as articles in the Record and in American reviews. He was a man of varied acquirements. His hymns were set to his own melodies. He was an artist, a mechanic: his little workshop had its forge, its carpenter's bench, its printing press. To the end of his life his strong Calvinism, and his dread of mere external union in church government, kept him distinct from all movements of church comprehension, though freely joining in communion with all the sections of Evangelical thought in Geneva and Scotland. At one time there seemed a prospect of his even rejoining the national Church, which had driven him from her. One of his greatest joys was the meeting of the Evangelical Alliance at Geneva (1861). He left no sect; one of his latest orders was the demolition of his decayed chapel, in which he had preached for 43 years. He died at Vandoeuvres, near Geneva, in 1864, leaving a numerous family, one of whom, the Rev. S. C. Malan, D.D., sometime Vicar of Broadwindsor, is well known as a linguist and a theologian of the English Church. To English readers Malan is chiefly known as a hymn-writer through translations of his "Non, ce n'est pas mourir" (q.v.): "It is not death to die", &c. About a dozen of his hymns appear in a translated form in the Friendly Visitor for 1826. [Rev. H. Leigh Bennett, M.A.]
-- John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology (1907)
=================
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/César_Malan
César Malan
Henry Hart Milman

1791 - 1868 Person Name: Henry H. Milman Hymnal Number: 316 Author of "Ride On, Ride On in Majesty" in Voices Together Milman, Henry Hart, D.D., the youngest son of Sir Francis Milman (who received his Baronetage as an eminent Court physician), was born Feb. 10th, 1791, and educated at Dr. Burney's at Greenwich, and subsequently at Eton. His career at B. N. C. Oxford, was brilliant. He took a first class in classics, and carried off the Newdigate, Latin Verse, Latin Essay, and English Essay. His Newdigate on the Apollo Belvedere, 1812, is styled by Dean Stanley "the most perfect of Oxford prize poems." His literary career for several years promised to be poetical. His tragedy Fazio was played at Covent Garden, Miss O'Neill acting Bianca. Samor was written in the year of his appointment to St. Mary's, Reading (1817); The Fall of Jerusalem (1820); Belshazzar and The Martyr of Antioch (1822), and Anne Boleyn, gained a brilliant reception from the reviewers and the public. He was appointed Poetry Professor at Oxford in 1821, and was succeeded ten years after by Keble. It must have been before 1823, the date of Heber's consecration to Calcutta, that the 13 hymns he contributed to Heber's Hymns were composed. But his poetry was only the prelude to his larger work.
The Bampton Lectures (1827) mark his transition to theological study, and the future direction of it was permanently fixed by his History of the Jews (1829). This book raised a storm of obloquy. It was denounced from the University pulpit, and in the British Critic. "It was the first decisive inroad of German theology into England, the first palpable indication that the Bible could be studied like another book, that the characters and events of the sacred history could be treated at once critically and reverently" (Dean Stanley).
In 1835 he was presented by Sir Robert Peel to a Canonry at Westminster and the Rectory of St. Margaret's. In 1839 appeared his valuable edition of Gibbon's Decline and Fall; and in 1840 his History of Christianity to the Abolition of Paganism in the Roman Empire. Among his minor works in a different field were his Life of Keats and his edition and Life of Horace. It was not till 1854 that his greatest work—-for "vast and varied learning, indefatigable industry, calm impartiality, and subtle and acute criticism, among the most memorable in our language" (Quart Rev.)—-Latin Christianity—-appeared. He had been appointed Dean of St. Paul's in 1849. The great services under the dome originated in his tenure of the Deanery. His latest work, published after his death, Sept. 24, 1868, was The Annals of St. Paul’s. Though one of the most illustrious in the school of English liberal theology, he had no sympathy with the extreme speculations of Germany. The "criticism" of Tübingen "will rarely bear criticism." He "should like an Ewald to criticise Ewald." "Christianity will survive the criticism of Dr. Strauss," and the "bright flashing artillery" of Rénan. His historical style has been compared to Gibbon in its use of epigram and antithesis. His narrative is full of rapidity of movement. His long complex paragraphs have often a splendour of imagination as well as wealth of thought. All the varied powers of his mind found vent in his conversation; he was called, after his death, "the last of the great converters." The catalogue of his friends from the days of Heber, "his early friend," to those of Hallam, Macaulay, and Dean Stanley, was long and distinguished.
Milman's 13 hymns were published in Heber's posthumous Hymns in 1827, and subsequently in his own Selection of Psalms & Hymns, 1837. The fine hymn for The Burial of the Dead, in Thring's Collection, "Brother, thou art gone before us," is from The Martyr of Antioch (1822). Like Heber's, they aim at higher literary expression and lyric grace. He makes free use of refrains. The structure is often excellent. His style is less florid and fuller of burning, sometimes lurid force than Heber's. His hymn for the 16th Sunday after Trinity, "When our heads are bowed with woe," has no peer in its presentation of Christ's human sympathy; the hymn for the 2nd Sunday in Lent, “Oh! help us, Lord! each hour of need," is a piece of pure deep devotion. "Ride on, ride on in majesty," the hymn for Palm Sunday, is one of our best hymns. And the stanzas for Good Friday, "Bound upon the accursed tree," form one of the finest meditations on the Passion. All his hymns are still in common use. [Rev.H.Leigh Bennett, M.A.]
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology (1907)
Henry Hart Milman
Charles V. Stanford

1852 - 1924 Hymnal Number: 83 Composer of "ENGELBERG" in Voices Together Sir Charles Villiers Stanford (30 September 1852 – 29 March 1924) was an Irish composer, teacher and conductor. Born to a well-off and highly musical family in Dublin, Stanford was educated at the University of Cambridge before studying music in Leipzig and Berlin. He was instrumental in raising the status of the Cambridge University Musical Society, attracting international stars to perform with it.
While still an undergraduate, Stanford was appointed organist of Trinity College, Cambridge. In 1882, aged 29, he was one of the founding professors of the Royal College of Music, where he taught composition for the rest of his life. From 1887 he was also the professor of music at Cambridge. As a teacher, Stanford was sceptical about modernism, and based his instruction chiefly on classical principles as exemplified in the music of Brahms. Among his pupils were rising composers whose fame went on to surpass his own, such as Gustav Holst and Ralph Vaughan Williams. As a conductor, Stanford held posts with the Bach Choir and the Leeds triennial music festival.
Stanford composed a substantial number of concert works, including seven symphonies, but his best-remembered pieces are his choral works for church performance, chiefly composed in the Anglican tradition. He was a dedicated composer of opera, but none of his nine completed operas has endured in the general repertory. Some critics regarded Stanford, together with Hubert Parry and Alexander Mackenzie, as responsible for a renaissance in English music. However, after his conspicuous success as a composer in the last two decades of the 19th century, his music was eclipsed in the 20th century by that of Edward Elgar as well as former pupils.
Stanford was born in Dublin, the only son of John James Stanford and his second wife, Mary, née Henn. John Stanford was a prominent Dublin lawyer, Examiner to the Court of Chancery in Ireland and Clerk of the Crown for County Meath. His wife was the third daughter of William Henn, Master of the High Court of Chancery in Ireland. Both parents were accomplished amateur musicians; John Stanford was a cellist and a noted bass singer who was chosen to perform the title role in Mendelssohn's Elijah at the Irish premiere in 1847. Mary Stanford was an amateur pianist, capable of playing the solo parts in concertos at Dublin concerts.
The young Stanford was given a conventional education at a private day school in Dublin run by Henry Tilney Bassett, who concentrated on the classics to the exclusion of other subjects. Stanford's parents encouraged the boy's precocious musical talent, employing a succession of teachers in violin, piano, organ and composition. Three of his teachers were former pupils of Ignaz Moscheles, including his godmother Elizabeth Meeke, of whom Stanford recalled, "She taught me, before I was twelve years old, to read at sight. … She made me play every day at the end of my lesson a Mazurka of Chopin: never letting me stop for a mistake. … By the time I had played through the whole fifty-two Mazurkas, I could read most music of the calibre my fingers could tackle with comparative ease." One of the young Stanford's earliest compositions, a march in D♭ major, written when he was eight years old, was performed in the pantomime at the Theatre Royal, Dublin three years later. At the age of nine, Stanford gave a piano recital for an invited audience, playing works by Beethoven, Handel, Mendelssohn, Moscheles, Mozart and Bach. One of his songs was taken up by the University of Dublin Choral Society and was well received.
In the 1860s Dublin received occasional visits from international stars, and Stanford was able to hear famous performers such as Joseph Joachim, Henri Vieuxtemps and Adelina Patti. The annual visit of the Italian Opera Company from London, led by Giulia Grisi, Giovanni Matteo Mario and later Thérèse Tietjens, gave Stanford a taste for opera that remained with him all his life. When he was ten, his parents took him to London for the summer, where he stayed with his mother's uncle in Mayfair. While there he took composition lessons from the composer and teacher Arthur O'Leary, and piano lessons from Ernst Pauer, professor of piano at the Royal Academy of Music (RAM). On his return to Dublin, his godmother having left Ireland, he took lessons from Henrietta Flynn, another former Leipzig Conservatory pupil of Moscheles, and later from Robert Stewart, organist of St Patrick's Cathedral, as well as from a third Moscheles pupil, Michael Quarry. During his second spell in London two years later, he met the composer Arthur Sullivan and the musical administrator and writer George Grove, who later played important parts in his career.
John Stanford hoped that his son would follow him into the legal profession but accepted his decision to pursue music as a career. However, he stipulated that Stanford should have a conventional university education before going on to musical studies abroad. Stanford tried unsuccessfully for a classics scholarship at Trinity Hall, Cambridge, but gained an organ scholarship, and later a classics scholarship, at Queens' College. By the time he went up to Cambridge he had written a substantial number of compositions, including vocal music, both sacred and secular, and orchestral works (a rondo for cello and orchestra and a concert overture).
Stanford immersed himself in the musical life of the university to the detriment of his Latin and Greek studies. He composed religious and secular vocal works, a piano concerto, and incidental music for Longfellow's play A Spanish Student. In November 1870 he appeared as piano soloist with the Cambridge University Musical Society (CUMS), and quickly became its assistant conductor and a committee member. The society had declined in excellence since its foundation in 1843. Its choir consisted solely of men and boys; the lack of women singers severely limited the works that the society could present. Stanford was unable to persuade the members to admit women, and so he staged what The Musical Times called "a bloodless revolution." In February 1872 he co-founded a mixed choir, the Amateur Vocal Guild, whose performances immediately put those of the CUMS singers in the shade. The members of CUMS rapidly changed their minds, and agreed to a merger of the two choirs, with women given associate membership of the society.
The conductor of the combined choir was John Larkin Hopkins, who was also organist of Trinity College. He became ill, and handed over the conductorship to Stanford in 1873. Stanford was also appointed Hopkins's deputy organist at Trinity, and moved from Queens' to Trinity in April 1873. In the summer of that year Stanford made his first trip to continental Europe. He went to Bonn for the Schumann Festival held there, where he met Joachim and Brahms. His growing love of the music of Schumann and Brahms marked him as a classicist at a time when many music-lovers were divided into the classical or the modernist camps, the latter represented by the music of Liszt and Wagner. Stanford was not constrained by the fashion for belonging to one camp or the other; he immensely admired Die Meistersinger though he was unenthusiastic about some of Wagner's other works. After leaving Bonn he returned home by way of Switzerland and then Paris, where he saw Meyerbeer's Le prophète.
Hopkins's illness proved fatal, and after his death the Trinity authorities invited Stanford to take over as organist of the college. He accepted with the proviso that he was to be released each year for a spell of musical study in Germany. The fellows of the college resolved on 21 February 1874:
Two days after his appointment, Stanford took the final examinations for his classics degree. He ranked 65th of 66, and was awarded a third-class degree.
On the recommendation of Sir William Sterndale Bennett, former professor of music at Cambridge and now director of the Royal Academy of Music, Stanford went to Leipzig in the summer of 1874 for lessons with Carl Reinecke, professor of composition and piano at the Leipzig Conservatory. The composer Thomas Dunhill commented that by 1874 it was "the tail-end of the Leipzig ascendancy, when the great traditions of Mendelssohn had already begun to fade." Nevertheless, Stanford did not seriously consider studying anywhere else. Neither Dublin nor London offered any comparable musical training; the most prestigious British music school, the RAM, was at that time hidebound and reactionary. He was dismayed to find in Leipzig that Bennett had recommended him to a German pedant no more progressive than the teachers at the RAM. Stanford said of Reinecke, "Of all the dry musicians I have ever known he was the most desiccated. He had not a good word for any contemporary composer… He loathed Wagner … sneered at Brahms and had no enthusiasm of any sort." Stanford's biographer Paul Rodmell suggests that Reinecke's ultra-conservatism may have been unexpectedly good for his pupil "as it may have encouraged Stanford to kick against the traces." During his time in Leipzig Stanford took piano lessons from Robert Papperitz (1826–1903), organist of the city's Nikolaikirche, whom he found more helpful.
Among Stanford's compositions in 1874 was a setting of part one of Longfellow's poem "The Golden Legend." He intended to set the entire poem, but gave up, defeated by Longfellow's "numerous but unconnected characters." Stanford ignored this and other early works when assigning opus numbers in his mature years. The earliest compositions in his official list of works are a four-movement Suite for piano and a Toccata for piano, which both date from 1875.
After a second spell in Leipzig with Reinecke in 1875, which was no more productive than the first, Stanford was recommended by Joachim to study in Berlin the following year with Friedrich Kiel, whom Stanford found "a master at once sympathetic and able … I learnt more from him in three months, than from all the others in three years."
Returning to Cambridge in the intervals of his studies in Germany, Stanford had resumed his work as conductor of CUMS. He found the society in good shape under his deputy, Eaton Faning, and able to tackle demanding new works. In 1876 the society presented one of the first performances in Britain of the Brahms Requiem. In 1877 CUMS came to national attention when it presented the first British performance of Brahms's First Symphony.
During the same period, Stanford was becoming known as a composer. He was composing prolifically, though he later withdrew some of his works from these years, including a violin concerto which, according to Rodmell, suffered from "undistinguished thematic material." In 1875 his First Symphony won the second prize in a competition held at the Alexandra Palace for symphonies by British composers, although he had to wait a further two years to hear the work performed. In the same year Stanford directed the first performance of his oratorio "The Resurrection," given by CUMS. At the request of Alfred Tennyson, he wrote incidental music for Tennyson's drama Queen Mary, performed at the Lyceum Theatre, London in April 1876.
In April 1878, despite the disapproval of his father, Stanford married Jane Anna Maria Wetton, known as Jennie, a singer whom he had met when she was studying in Leipzig. They had a daughter, Geraldine Mary, born in 1883 and a son, Guy Desmond, born in 1885.
In 1878 and 1879 Stanford worked on his first opera, The Veiled Prophet, to a libretto by his friend William Barclay Squire. It was based on a poem by Thomas Moore with characters including a virgin priestess and a mystic prophet, and a plot that culminates in poisoning and stabbing. Stanford offered the work to the opera impresario Carl Rosa, who refused it and suggested that the composer should try to have it staged in Germany: "Its success will (unfortunately) have much greater chances here if accepted abroad." Referring to the enormous popularity of Sullivan's comic operas, Rosa added, "If the work was of the Pinafore style it would be quite another matter." Stanford had greatly enjoyed Sullivan's Cox and Box, but The Veiled Prophet was intended to be a serious work of high drama and romance. Stanford had made many useful contacts during his months in Germany, and his friend the conductor Ernst Frank got the piece staged at the Königliches Schauspiel in Hanover in 1881. Reviewing the premiere for The Musical Times, Stanford's friend J A Fuller Maitland wrote, "Mr. Stanford's style of instrumentation … is built more or less on that of Schumann; while his style of dramatic treatment bears more resemblance to Meyerbeer than to that of any other master." Other reviews were mixed, and the opera had to wait until 1893 for its English premiere. Stanford nevertheless continued to seek operatic success throughout his career. In his lifelong enthusiasm for opera he differed strikingly from his contemporary Hubert Parry, who made one attempt at composing opera and then renounced the genre.
By the early 1880s, Stanford was becoming a major figure in the British musical scene. His only major rivals were seen as Sullivan, Frederic Hymen Cowen, Parry, Alexander Mackenzie and Arthur Goring Thomas. Sullivan was by this time viewed with suspicion in high-minded musical circles for composing comic rather than grand operas; Cowen was regarded more as a conductor than as a composer; and the other three, though seen as promising, had not so far made a clear mark as Stanford had done. Stanford helped Parry in particular to gain recognition, commissioning incidental music from him for a Cambridge production of Aristophanes' The Birds and a symphony (the "Cambridge") for the musical society. At Cambridge Stanford continued to raise the profile of CUMS, as well as his own, by securing appearances by leading international musicians including Joachim, Hans Richter, Alfredo Piatti and Edward Dannreuther. The society attracted further attention by premiering works by Cowen, Parry, Mackenzie, Goring Thomas and others. Stanford was also making an impression in his capacity as organist of Trinity, raising musical standards and composing what his biographer Jeremy Dibble calls "some highly distinctive church music" including a Service in B♭ (1879), the anthem "The Lord is my shepherd" (1886) and the motet Justorum animae (1888).
In the first half of the 1880s, Stanford collaborated with the author Gilbert à Beckett on two operas, Savonarola, and The Canterbury Pilgrims. The former was well received at its premiere in Hamburg in April 1884, but received a critical savaging when staged at Covent Garden in July of the same year. Parry commented privately, "It seems very badly constructed for the stage, poorly conceived and the music, though clean and well-managed, is not striking or dramatic." The most severe public criticism was in The Theatre, whose reviewer wrote, "The book of Savonarola is dull, stilted, and, from a dramatic point of view, weak. It is not, however, so crushingly tiresome as the music fitted to it. Savonarola has gone far to convince me that opera is quite out of [Stanford's] line and that the sooner he abandons the stage for the cathedral, the better for his musical reputation." The Canterbury Pilgrims had been premiered in London in April 1884, three months before Savonarola was presented at Covent Garden. It had a better reception than the latter, though reviews pointed out Stanford's debt to Die Meistersinger, and complained of a lack of emotion in the love music. George Grove agreed with the critics, writing to Parry, "Charlie's music contains everything but sentiment. Love not at all – that I heard not a grain of. … And I do think that there might be more tune. Melody is not a thing to be avoided surely." In 1896 a critic wrote that the opera had "just such a 'book' as would have suited the late Alfred Cellier. He would probably have made of it a charming light English opera. But Dr. Stanford has chosen to use it for the exemplification of those advanced theories which we know him to hold, and he has given us music which would incline us to think that Die Meistersinger had been his model. The effect of the combination is not happy."
In 1883, the Royal College of Music was set up to replace the short-lived and unsuccessful National Training School for Music (NTSM). Neither the NTSM nor the longer-established Royal Academy of Music had provided adequate musical training for professional orchestral players, and the founder-director of the college, George Grove, was determined that the new institution should succeed in doing so. His two principal allies in this undertaking were the violinist Henry Holmes and Stanford. In a study of the founding of the college, David Wright notes that Stanford had two main reasons for supporting Grove's aim. The first was his belief that a capable college orchestra was essential to give students of composition the chance to experience the sound of their music. His second reason was the severe contrast between the competence of German orchestras and the performance of their British counterparts. He accepted Grove's offer of the posts of professor of composition and (with Holmes) conductor of the college orchestra. He held the professorship for the rest of his life; among the best known of his many pupils were Samuel Coleridge-Taylor, Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, John Ireland, Frank Bridge and Arthur Bliss.
Stanford was never an easy-going teacher. He insisted on one-to-one tutorials, and worked his pupils hard. One of them, Herbert Howells, recalled, "Corner any Stanford pupil you like, and ask him to confess the sins he most hated being discovered in by his master. He will tell you 'slovenliness' and 'vulgarity.' When these went into the teacher's room they came out, badly damaged. Against compromise with dubious material or workmanship Stanford stubbornly set his face." Another pupil, Edgar Bainton, recalled:
Stanford's teaching seemed to be without method or plan. His criticism consisted for the most part of "I like it, my boy," or "It's damned ugly, my boy" (the latter in most cases). In this, perhaps, lay its value. For in spite of his conservatism, and he was intensely and passionately conservative in music as in politics, his amazingly comprehensive knowledge of musical literature of all nations and ages made one feel that his opinions, however irritating, had weight.
To Stanford's regret, many of his pupils who achieved eminence as composers broke away from his classical, Brahmsian precepts, as he had himself rebelled against Reinecke's conservatism. The composer George Dyson wrote, "In a certain sense the very rebellion he fought was the most obvious fruit of his methods. And in view of what some of these rebels have since achieved, one is tempted to wonder whether there is really anything better a teacher can do for his pupils than drive them into various forms of revolution." The works of some of Stanford's pupils, including Holst and Vaughan Williams, entered the general repertory in Britain, and to some extent elsewhere, as Stanford's never did. For many years after his death it seemed that Stanford's greatest fame would be as a teacher. Among his achievements at the RCM was the establishment of an opera class, with at least one operatic production every year. From 1885 to 1915 there were 32 productions, all of them conducted by Stanford.
In 1887 Stanford was appointed professor of music at Cambridge in succession to Sir George Macfarren who died in October of that year. Up to this time, the university had awarded music degrees to candidates who had not been undergraduates at Cambridge; all that was required was to pass the university's music examinations. Stanford was determined to end the practice, and after six years he persuaded the university authorities to agree. Three years' study at the university became a prerequisite for sitting the bachelor of music examinations.
During the last decades of the 19th century, Stanford's academic duties did not prevent him from composing or performing. He was appointed conductor of the Bach Choir, London, in 1885, succeeding its founding conductor Otto Goldschmidt. He held the post until 1902. Hans von Bülow conducted the German premiere of Stanford's Irish Symphony in Hamburg in January 1888, and was sufficiently impressed by the work to programme it in Berlin shortly afterwards. Richter conducted it in Vienna, and Mahler later conducted it in New York. For the Theatre Royal, Cambridge, Stanford composed incidental music for productions of Aeschylus's The Eumenides (1885), and Sophocles' Oedipus Tyrannos (1887). The Times said of the former, "Mr. Stanford's music is dramatically significant, as well as beautiful in itself. It has, moreover, that quality so rare among modern composers – style." In both sets of music Stanford made extensive use of leitmotifs, in the manner of Wagner; the critic of The Times noted the Wagnerian character of the prelude to Oedipus.
In the 1890s, Bernard Shaw writing as "Corno di Bassetto", music critic of The World, voiced mixed feelings about Stanford. In Shaw's view, the best of Stanford's works displayed an uninhibited, Irish, character. The critic was dismissive of the composer's solemn Victorian choral music. In July 1891, Shaw's column was full of praise for Stanford's capacity for spirited tunes, declaring that Richard D'Oyly Carte should engage him to succeed Sullivan as the composer of Savoy operas. In October of the same year, Shaw attacked Stanford's oratorio Eden, bracketing the composer with Parry and Mackenzie as a mutual admiration society, purveying "sham classics":
[W]ho am I that I should be believed, to the disparagement of eminent musicians? If you doubt that Eden is a masterpiece, ask Dr Parry and Dr Mackenzie, and they will applaud it to the skies. Surely Dr Mackenzie’s opinion is conclusive; for is he not the composer of Veni Creator, guaranteed as excellent music by Professor Stanford and Dr Parry? You want to know who Parry is? Why, the composer of "Blest Pair of Sirens," as to the merits of which you only have to consult Dr Mackenzie and Professor Stanford.
To Fuller Maitland, the trio of composers lampooned by Shaw were the leaders of an English musical renaissance (although neither Stanford nor Mackenzie was English). This view persisted in some academic circles for many years.
Stanford returned to opera in 1893, with an extensively revised and shortened version of The Veiled Prophet. It had its British premiere at Covent Garden in July. His friend Fuller Maitland was by this time the chief music critic of The Times, and the paper's review of the opera was laudatory. According to Fuller Maitland The Veiled Prophet was the best novelty of an opera season that had also included Leoncavallo's Pagliacci, Bizet's Djamileh and Mascagni's I Rantzau. Stanford's next opera was Shamus O'Brien (1896), a comic opera to a libretto by George H. Jessop. The conductor was the young Henry Wood, who recalled in his memoirs that the producer, Sir Augustus Harris, managed to quell the dictatorial composer and prevent him from interfering with the staging. Stanford attempted to give Wood lessons in conducting, but the young man was unimpressed. The opera was successful, running for 82 consecutive performances. The work was given in German translation in Breslau in 1907; Thomas Beecham thought it "a colourful, racy work", and revived it in his 1910 opéra comique season at His Majesty's Theatre, London.
At the end of 1894, Grove retired from the Royal College of Music. Parry was chosen to succeed him, and although Stanford wholeheartedly congratulated his friend on his appointment, their relations soon deteriorated. Stanford was known as a hot-tempered and quarrelsome man. Grove had written of a board meeting at the Royal College "where somehow the spirit of the d----l himself had been working in Stanford all the time – as it sometimes does, making him so nasty and quarrelsome and contradictious as no one but he can be! He is a most remarkably clever and able fellow, full of resource and power – no doubt of that – but one has to purchase it often at a very dear price." Parry suffered worse at Stanford's hands with frequent rows, deeply upsetting to the highly-strung Parry. Some of their rows were caused by Stanford's reluctance to accept the authority of his old friend and protégé, but on other occasions Parry seriously provoked Stanford, notably in 1895 when he reduced the funding for Stanford's orchestral classes.
In 1898, Sullivan, ageing and unwell, resigned as conductor of the Leeds triennial music festival, a post which he had held since 1880. He believed that Stanford's motive for accepting the conductorship of the Leeds Philharmonic Society the previous year was to position himself to take over the festival. Stanford later felt obliged to write to The Times, denying that he had been party to a conspiracy to oust Sullivan. Sullivan was by then thought to be a dull conductor of other composers' music, and although Stanford's work as a conductor was not without its critics, he was appointed in Sullivan's place. He remained in charge until 1910. His compositions for the festival included "Songs of the Sea" (1904), "Stabat Mater" (1907) and "Songs of the Fleet (1910)." New works by other composers presented at Leeds during Stanford's years in charge included pieces by Parry, Mackenzie, and seven of Stanford's former pupils. The best-known new work from Stanford's time is probably Vaughan Williams's A Sea Symphony, premiered in 1910.
In 1901 Stanford returned once again to opera, with a version of Much Ado About Nothing, to a libretto by Julian Sturgis that was exceptionally faithful to Shakespeare's original. The Manchester Guardian commented, "Not even in the Falstaff of Arrigo Boito and Giuseppe Verdi have the characteristic charm, the ripe and pungent individuality of the original comedy been more sedulously preserved."
Despite good notices for the opera, Stanford's star was waning. In the first decade of the century, his music became eclipsed by that of a younger composer, Edward Elgar. In the words of the music scholar Robert Anderson, Stanford "had his innings with continental reputation in the latter decades of the nineteenth century, but then Elgar bowled him out." When Elgar was struggling for recognition in the 1890s, Stanford had been supportive of his younger colleague, conducting his music, putting him forward for a Cambridge doctorate, and proposing him for membership of the exclusive London club, the Athenaeum. He was, however, put out when Elgar's success at home and abroad eclipsed his own, with Richard Strauss (whom Stanford detested) praising Elgar as the first progressive English composer. When Elgar was appointed professor of music at Birmingham University in 1904, Stanford wrote him a letter that the recipient found "odious". Elgar retaliated in his inaugural lecture with remarks about composers of rhapsodies, widely seen as denigrating Stanford. Stanford later counter-attacked in his book A History of Music, writing of Elgar, "Cut off from his contemporaries by his religion and his want of regular academic training, he was lucky enough to enter the field and find the preliminary ploughing done."
Though bitter about being sidelined, Stanford continued to compose. Between the turn of the century and the outbreak of the First World War in 1914 his new works included a violin concerto (1901), a clarinet concerto (1902), a sixth and a seventh (and last) symphony (1906 and 1911), and his second piano concerto (1911). In 1916 he wrote his penultimate opera, The Critic. It was a setting of Sheridan's comedy of the same name, with the original text left mostly intact by the librettist, Lewis Cairns James. The work was well received at the premiere at the Shaftesbury Theatre, London, and was taken up later in the year by Beecham, who staged it in Manchester and London.
The First World War had a severe effect on Stanford. He was frightened by air-raids, and had to move from London to Windsor to avoid them. Many of his former pupils were casualties of the fighting, including Arthur Bliss, injured, Ivor Gurney, gassed, and George Butterworth, killed. The annual RCM operatic production, which Stanford had supervised and conducted every year since 1885, had to be cancelled. His income declined, as the fall in student numbers at the college reduced the demand for his services. After a serious disagreement at the end of 1916, his relationship with Parry deteriorated to the point of hostility. Stanford's magnanimity, however, came to the fore when Parry died two years later and Stanford successfully lobbied for him to be buried in St Paul's Cathedral.
After the war, Stanford handed over much of the direction of the RCM's orchestra to Adrian Boult, but continued to teach at the college. He gave occasional public lectures, including one on "Some Recent Tendencies in Composition", in January 1921 which was belligerently hostile to most of the music of the generation after his own. His last public appearance was on 5 March 1921 conducting the Royal Choral Society in his new cantata, At the Abbey Gate. Reviews were polite but unenthusiastic. The Times said, "we could not feel that the music had enough emotion behind it", The Observer thought it "quite appealing even though one feels it to be more facile than powerful."
In September 1922, Stanford completed the sixth Irish Rhapsody, his final work. Two weeks later he celebrated his 70th birthday; thereafter his health declined. On 17 March 1924 he suffered a stroke and on 29 March he died at his home in London, survived by his wife and children. He was cremated at Golders Green Crematorium on 2 April and his ashes were buried in Westminster Abbey the following day. The orchestra of the Royal College of Music, conducted by Boult, played music by Stanford, ending the service with a funeral march that he had written for Tennyson's Becket in 1893. The grave is in the north choir aisle of the Abbey, near the graves of Henry Purcell, John Blow and William Sterndale Bennett. The Times said, "the conjunction of the music of Stanford with that of his great predecessors showed how thoroughly as composer he belonged to their line."
Stanford's last opera, The Travelling Companion, composed during the war, was premiered by amateur performers at the David Lewis Theatre, Liverpool in 1925 with a reduced orchestra. The work was given complete at Bristol in 1928 and at Sadler's Wells Theatre, London, in 1935.
Stanford received many honours, including honorary doctorates from Oxford (1883), Cambridge (1888), Durham (1894), Leeds (1904), and Trinity College, Dublin (1921). He was knighted in 1902 and in 1904 was elected a member of the Royal Academy of Arts, Berlin.
In Stanford's music the sense of style, the sense of beauty, the feeling of a great tradition is never absent. His music is in the best sense of the word Victorian, that is to say it is the musical counterpart of the art of Tennyson, Watts and Matthew Arnold.
Stanford composed about 200 works, including seven symphonies, about 40 choral works, nine operas, 11 concertos and 28 chamber works, as well as songs, piano pieces, incidental music, and organ works. He suppressed most of his earliest compositions; the earliest of works that he chose to include in his catalogue date from 1875.
Throughout his career as a composer, Stanford's technical mastery was rarely in doubt. The composer Edgar Bainton said of him, "Whatever opinions may be held upon Stanford's music, and they are many and various, it is, I think, always recognised that he was a master of means. Everything he turned his hand to always 'comes off.'" On the day of Stanford's death, one former pupil, Gustav Holst, said to another, Herbert Howells, "The one man who could get any one of us out of a technical mess is now gone from us."
After Stanford's death most of his music was quickly forgotten, with the exception of his works for church performance. His Stabat Mater and Requiem held their place in the choral repertoire, the latter championed by Sir Thomas Beecham. Stanford's two sets of sea songs and the song "The Blue Bird" were still performed from time to time, but even his most popular opera, Shamus O'Brien came to seem old fashioned with its "stage-Irish" vocabulary. However, in his 2002 study of Stanford Dibble writes that the music, increasingly available on disc if not in live performance, still has the power to surprise. In Dibble's view, the frequent charge that Stanford is "Brahms and water" was disproved once the symphonies and concertos, much of the chamber music and many of the songs became available for reappraisal when recorded for compact disc. In 2002, Rodmell's study of Stanford included a discography running to 16 pages.
The criticism most often made of Stanford's music by writers from Shaw onwards is that his music lacks passion. Shaw praised "Stanford the Celt" and abominated "Stanford the Professor", who reined in the emotions of the Celt. In Stanford's church music, the critic Nicholas Temperley finds "a thoroughly satisfying artistic experience, but one that is perhaps lacking in deeply felt religious impulse." In his operas and elsewhere, Grove, Parry and later commentators found music that ought to convey love and romance failing to do so. Like Parry, Stanford strove for seriousness, and his competitive streak led him to emulate Sullivan not in comic opera, for which Stanford had a real gift, but in oratorio in what Rodmell calls grand statements that "only occasionally matched worthiness with power or profundity."
--excerpts from en.wikipedia.org
Charles V. Stanford
Juan Bautista Cabrera Ivars

1837 - 1916 Person Name: Juan Bautista Cabrera Hymnal Number: 346 Translator (Spanish) of "Christ the Lord Is Risen Today (El Señor resucitó)" in Voices Together Juan Bautista Cabrera Ivars was born in Benisa, Spain, April 23, 1837. He attended seminary in Valencia, studying Hebrew and Greek, and was ordained as a priest. He fled to Gibraltar in 1863 due to religious persecution where he abandoned Catholicism. He worked as a teacher and as a translator. One of the works he translated was E.H. Brown's work on the thirty-nine articles of the Anglican Church, which was his introduction to Protestantism. He was a leader of a Spanish Reformed Church in Gibraltar. He continued as a leader in this church when he returned to Spain after the government of Isabel II fell, but continued to face legal difficulties. He then organized the Spanish Reformed Episcopal Church and was consecrated as bishop in 1894. He recognized the influence of music and literature on evangelism which led him to write and translate hymns.
Dianne Shapiro, from Real Academia de la Historia (https://dbe.rah.es/biografias/39825/juan-bautista-cabrera-ivars) and Himnos Cristanos (https://www.himnos-cristianos.com/biografia-juan-bautista-cabrera/) (accessed 7/30/2021)
Juan Bautista Cabrera Ivars
Thomas Andrew Dorsey

1899 - 1993 Person Name: Thomas A. Dorsey Hymnal Number: 610 Author of "Precious Lord, Take My Hand" in Voices Together Thomas Andrew Dorsey was born in Villa Rica, a small rural town near Atlanta, Georgia. In 1919 he moved to Chicago. Most of his musical training was in the church, but he also studied and played jazz and blues. He later combined jazz and blues with religious texts, giving birth to gospel music. In 1931, along with Magnolia Lewis-Butts and Theodore Roosevelt Frye, he established the first gospel choir at Ebenezer Baptist Church in Chicago. He went on to lead the gospel choir at Pilgrim Baptist Church, which he led for 60 years. Dorsey was also instrumental in founding the National Convention of Gospel Choirs and Choruses (NCGCC) in 1933. The convention taught choirs all over the country how to sing gospel music.
Dianne Shapiro, from "Gospel" in Encyclopedia of Chicago (accessed 8/12/2020)
Thomas Andrew Dorsey
Charles Albert Tindley

1851 - 1933 Person Name: Charles A. Tindley Hymnal Number: 311 Author of "We Are Often Tossed and Driven" in Voices Together Charles Albert Tindley was born in Berlin, Maryland, July 7, 1851; son of Charles and Hester Tindley. His father was a slave, and his mother was free. Hester died when he was very young; he was taken in my his mother’s sister Caroline Miller Robbins in order to keep his freedom. It seems that he was expected to work to help the family. In his Book of Sermons (1932), he speaks of being “hired out” as a young boy, “wherever father could place me.” He married Daisy Henry when he was seventeen. Together they had eight children, some of whom would later assist him with the publication of his hymns.
Tindley was largely self-taught throughout his lifetime. He learned to read mostly on his own. After he and Daisy moved to Philadelphia in 1875, he took correspondence courses toward becoming a Methodist minister. He did this while working as a sexton (building caretaker) for the East Bainbridge Street Church. Beginning in 1885, he was appointed by the local bishop to serve two or three-year terms at a series of churches, until coming full circle to become pastor at East Bainbridge in 1902. Under his leadership, the church grew rapidly. They relocated in 1904 to the East Calvary Methodist Episcopal Church, then again in 1924 to the new Tindley Temple, where the membership roll blossomed to about ten thousand.
Tindley was known for being a captivating preacher, and for also taking an active role in the betterment of the people in his community. His songs were an outgrowth of his preaching ministry, often introduced during his sermons. Tindley was able to draw people of multiple races to his church ministry; likewise, his songs have been adopted and proliferated by white and black churches alike.
The songs of Charles Tindley were published cumulatively in two editions of Soul Echoes (1905, 1909) and six editions of New Songs of Paradise (1916-1941).
His wife Daisy died in 1924, before the completion of the Tindley Temple. He remarried in 1927 to Jenny Cotton. Charles A. Tindley died July 26, 1933.
Charles Albert Tindley
Conrad Kocher

1786 - 1872 Hymnal Number: 120 Composer of "DIX" in Voices Together Trained as a teacher, Conrad Kocher (b. Ditzingen, Wurttemberg, Germany, 1786; d. Stuttgart, Germany, 1872) moved to St. Petersburg, Russia, to work as a tutor at the age of seventeen. But his love for the music of Haydn and Mozart impelled him to a career in music. He moved back to Germany in 1811, settled in Stuttgart, and remained there for most of his life. The prestigious Cotta music firm published some of his early compositions and sent him to study music in Italy, where he came under the influence of Palestrina's music. In 1821 Kocher founded the School for Sacred Song in Stuttgart, which popularized four-part singing in the churches of that region. He was organist and choir director at the Stiftskirche in Stuttgart from 1827 to 1865. Kocher wrote a treatise on church music, Die Tonkunst in der Kirche (1823), collected a large number of chorales in Zions Harfe (1855), and composed an oratorio, two operas, and some sonatas. William H. Monk created the current form of DIX by revising and shortening Conrad Kocher's chorale melody for “Treuer Heiland, wir sind hier,” found in Kocher's Stimmen aus dem Reiche Gottes (1838).
Bert Polman
Conrad Kocher
William Cowper

1731 - 1800 Hymnal Number: 618 Author of "Sometimes a Light Surprises" in Voices Together William Cowper (pronounced "Cooper"; b. Berkampstead, Hertfordshire, England, 1731; d. East Dereham, Norfolk, England, 1800) is regarded as one of the best early Romantic poets. To biographers he is also known as "mad Cowper." His literary talents produced some of the finest English hymn texts, but his chronic depression accounts for the somber tone of many of those texts. Educated to become an attorney, Cowper was called to the bar in 1754 but never practiced law. In 1763 he had the opportunity to become a clerk for the House of Lords, but the dread of the required public examination triggered his tendency to depression, and he attempted suicide. His subsequent hospitalization and friendship with Morley and Mary Unwin provided emotional stability, but the periods of severe depression returned. His depression was deepened by a religious bent, which often stressed the wrath of God, and at times Cowper felt that God had predestined him to damnation.
For the last two decades of his life Cowper lived in Olney, where John Newton became his pastor. There he assisted Newton in his pastoral duties, and the two collaborated on the important hymn collection Olney Hymns (1779), to which Cowper contributed sixty-eight hymn texts.
Bert Polman
============
Cowper, William, the poet. The leading events in the life of Cowper are: born in his father's rectory, Berkhampstead, Nov. 26, 1731; educated at Westminster; called to the Bar, 1754; madness, 1763; residence at Huntingdon, 1765; removal to Olney, 1768; to Weston, 1786; to East Dereham, 1795; death there, April 25, 1800.
The simple life of Cowper, marked chiefly by its innocent recreations and tender friendships, was in reality a tragedy. His mother, whom he commemorated in the exquisite "Lines on her picture," a vivid delineation of his childhood, written in his 60th year, died when he was six years old. At his first school he was profoundly wretched, but happier at Westminster; excelling at cricket and football, and numbering Warren Hastings, Colman, and the future model of his versification. Churchill, among his contemporaries or friends. Destined for the Bar, he was articled to a solicitor, along with Thurlow. During this period he fell in love with his cousin, Theodora Cowper, sister to Lady Hesketh, and wrote love poems to her. The marriage was forbidden by her father, but she never forgot him, and in after years secretly aided his necessities. Fits of melancholy, from which he had suffered in school days, began to increase, as he entered on life, much straitened in means after his father's death. But on the whole, it is the playful, humorous side of him that is most prominent in the nine years after his call to the Bar; spent in the society of Colman, Bonnell Thornton, and Lloyd, and in writing satires for The Connoisseur and St. James's Chronicle and halfpenny ballads. Then came the awful calamity, which destroyed all hopes of distinction, and made him a sedentary invalid, dependent on his friends. He had been nominated to the Clerkship of the Journals of the House of Lords, but the dread of appearing before them to show his fitness for the appointment overthrew his reason. He attempted his life with "laudanum, knife and cord,"—-in the third attempt nearly succeeding. The dark delusion of his life now first showed itself—a belief in his reprobation by God. But for the present, under the wise and Christian treatment of Dr. Cotton (q. v.) at St. Albans, it passed away; and the eight years that followed, of which the two first were spent at Huntingdon (where he formed his lifelong friendship with Mrs. Unwin), and the remainder at Olney in active piety among the poor, and enthusiastic devotions under the guidance of John Newton (q. v.), were full of the realisation of God's favour, and the happiest, most lucid period of his life. But the tension of long religious exercises, the nervous excitement of leading at prayer meetings, and the extreme despondence (far more than the Calvinism) of Newton, could scarcely have been a healthy atmosphere for a shy, sensitive spirit, that needed most of all the joyous sunlight of Christianity. A year after his brother's death, madness returned. Under the conviction that it was the command of God, he attempted suicide; and he then settled down into a belief in stark contradiction to his Calvinistic creed, "that the Lord, after having renewed him in holiness, had doomed him to everlasting perdition" (Southey). In its darkest form his affliction lasted sixteen months, during which he chiefly resided in J. Newton's house, patiently tended by him and by his devoted nurse, Mrs. Unwin. Gradually he became interested in carpentering, gardening, glazing, and the tendance of some tame hares and other playmates. At the close of 1780, Mrs. Unwin suggested to him some serious poetical work; and the occupation proved so congenial, that his first volume was published in 1782. To a gay episode in 1783 (his fascination by the wit of Lady Austen) his greatest poem, The Task, and also John Gilpin were owing. His other principal work was his Homer, published in 1791. The dark cloud had greatly lifted from his life when Lady Hesketh's care accomplished his removal to Weston (1786): but the loss of his dear friend William Unwin lowered it again for some months. The five years' illness of Mrs. Unwin, during which his nurse of old became his tenderly-watched patient, deepened the darkness more and more. And her death (1796) brought “fixed despair," of which his last poem, The Castaway, is the terrible memorial. Perhaps no more beautiful sentence has been written of him, than the testimony of one, who saw him after death, that with the "composure and calmness" of the face there “mingled, as it were, a holy surprise."
Cowper's poetry marks the dawn of the return from the conventionality of Pope to natural expression, and the study of quiet nature. His ambition was higher than this, to be the Bard of Christianity. His great poems show no trace of his monomania, and are full of healthy piety. His fame as a poet is less than as a letter-writer: the charm of his letters is unsurpassed. Though the most considerable poet, who has written hymns, he has contributed little to the development of their structure, adopting the traditional modes of his time and Newton's severe canons. The spiritual ideas of the hymns are identical with Newton's: their highest note is peace and thankful contemplation, rather than joy: more than half of them are full of trustful or reassuring faith: ten of them are either submissive (44), self-reproachful (17, 42, 43), full of sad yearning (1, 34), questioning (9), or dark spiritual conflict (38-40). The specialty of Cowper's handling is a greater plaintiveness, tenderness, and refinement. A study of these hymns as they stood originally under the classified heads of the Olney Hymns, 1779, which in some cases probably indicate the aim of Cowper as well as the ultimate arrangement of the book by Newton, shows that one or two hymns were more the history of his conversion, than transcripts of present feelings; and the study of Newton's hymns in the same volume, full of heavy indictment against the sins of his own regenerate life, brings out the peculiar danger of his friendship to the poet: it tends also to modify considerably the conclusions of Southey as to the signs of incipient madness in Cowper's maddest hymns. Cowper's best hymns are given in The Book of Praise by Lord Selborne. Two may be selected from them; the exquisitely tender "Hark! my soul, it is the Lord" (q. v.), and "Oh, for a closer walk with God" (q. v.). Anyone who knows Mrs. Browning's noble lines on Cowper's grave will find even a deeper beauty in the latter, which is a purely English hymn of perfect structure and streamlike cadence, by connecting its sadness and its aspiration not only with the “discord on the music" and the "darkness on the glory," but the rapture of his heavenly waking beneath the "pathetic eyes” of Christ.
Authorities. Lives, by Hayley; Grimshaw; Southey; Professor Goldwin Smith; Mr. Benham (attached to Globe Edition); Life of Newton, by Rev. Josiah Bull; and the Olney Hymns. The numbers of the hymns quoted refer to the Olney Hymns. [Rev. H. Leigh Bennett, M.A.]
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology (1907)
================
Cowper, W. , p. 265, i. Other hymns are:—
1. Holy Lord God, I love Thy truth. Hatred of Sin.
2. I was a grovelling creature once. Hope and Confidence.
3. No strength of nature can suffice. Obedience through love.
4. The Lord receives His highest praise. Faith.
5. The saints should never be dismayed. Providence. All these hymns appeared in the Olney Hymns, 1779.
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology, Appendix, Part II (1907)
=====================
Cowper, W., p. 265, i. Prof. John E. B. Mayor, of Cambridge, contributed some letters by Cowper, hitherto unpublished, together with notes thereon, to Notes and Queries, July 2 to Sept. 24, 1904. These letters are dated from Huntingdon, where he spent two years after leaving St. Alban's (see p. 265, i.), and Olney. The first is dated "Huntingdon, June 24, 1765," and the last "From Olney, July 14, 1772." They together with extracts from other letters by J. Newton (dated respectively Aug. 8, 1772, Nov. 4, 1772), two quotations without date, followed by the last in the N. & Q. series, Aug. 1773, are of intense interest to all students of Cowper, and especially to those who have given attention to the religious side of the poet's life, with its faint lights and deep and awful shadows. From the hymnological standpoint the additional information which we gather is not important, except concerning the hymns "0 for a closer walk with God," "God moves in a mysterious way," "Tis my happiness below," and "Hear what God, the Lord, hath spoken." Concerning the last three, their position in the manuscripts, and the date of the last from J. Newton in the above order, "Aug. 1773," is conclusive proof against the common belief that "God moves in a mysterious way" was written as the outpouring of Cowper's soul in gratitude for the frustration of his attempted suicide in October 1773.
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology, New Supplement (1907)
William Cowper

 My Starred Hymns
My Starred Hymns


