Planning worship?
Check out our sister site, ZeteoSearch.org,
for 20+ additional resources related to your search.
- |
User Links
Person Results
‹ Return to hymnal









Export as CSV
Johann Sebastian Bach

1685 - 1750 Hymnal Number: 247 Arranger of "PASSION CHORALE" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Johann Sebastian Bach was born at Eisenach into a musical family and in a town steeped in Reformation history, he received early musical training from his father and older brother, and elementary education in the classical school Luther had earlier attended.
Throughout his life he made extraordinary efforts to learn from other musicians. At 15 he walked to Lüneburg to work as a chorister and study at the convent school of St. Michael. From there he walked 30 miles to Hamburg to hear Johann Reinken, and 60 miles to Celle to become familiar with French composition and performance traditions. Once he obtained a month's leave from his job to hear Buxtehude, but stayed nearly four months. He arranged compositions from Vivaldi and other Italian masters. His own compositions spanned almost every musical form then known (Opera was the notable exception).
In his own time, Bach was highly regarded as organist and teacher, his compositions being circulated as models of contrapuntal technique. Four of his children achieved careers as composers; Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven, Mendelssohn, Schumann, Brahms, and Chopin are only a few of the best known of the musicians that confessed a major debt to Bach's work in their own musical development. Mendelssohn began re-introducing Bach's music into the concert repertoire, where it has come to attract admiration and even veneration for its own sake.
After 20 years of successful work in several posts, Bach became cantor of the Thomas-schule in Leipzig, and remained there for the remaining 27 years of his life, concentrating on church music for the Lutheran service: over 200 cantatas, four passion settings, a Mass, and hundreds of chorale settings, harmonizations, preludes, and arrangements. He edited the tunes for Schemelli's Musicalisches Gesangbuch, contributing 16 original tunes. His choral harmonizations remain a staple for studies of composition and harmony. Additional melodies from his works have been adapted as hymn tunes.
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology (1907)
Johann Sebastian Bach
Joseph Haydn

1732 - 1809 Person Name: Franz Joseh Haydn Hymnal Number: 269 Composer of "ST. ALBAN" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Franz Joseph Haydn (b. Rohrau, Austria, 1732; d. Vienna, Austria, 1809) Haydn's life was relatively uneventful, but his artistic legacy was truly astounding. He began his musical career as a choirboy in St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna, spent some years in that city making a precarious living as a music teacher and composer, and then served as music director for the Esterhazy family from 1761 to 1790. Haydn became a most productive and widely respected composer of symphonies, chamber music, and piano sonatas. In his retirement years he took two extended tours to England, which resulted in his "London" symphonies and (because of G. F. Handel's influence) in oratorios. Haydn's church music includes six great Masses and a few original hymn tunes. Hymnal editors have also arranged hymn tunes from various themes in Haydn's music.
Bert Polman
Joseph Haydn
C. Hubert H. Parry

1848 - 1918 Hymnal Number: 291 Composer of "RUSTINGTON" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Charles Hubert Hastings Parry KnBch/Brnt BMus United Kingdom 1848-1918. Born at Richmond Hill, Bournemouth, England, son of a wealthy director of the East India Company (also a painter, piano and horn musician, and art collector). His mother died of consumption shortly after his birth. His father remarried when he was three, and his stepmother favored her own children over her stepchildren, so he and two siblings were sometimes left out. He attended a preparatory school in Malvern, then at Twyford in Hampshire. He studied music from 1856-58 and became a pianist and composer. His musical interest was encouraged by the headmaster and by two organists. He gained an enduring love for Bach’s music from S S Wesley and took piano and harmony lessons from Edward Brind, who also took him to the ‘Three Choirs Festival in Hereford in 1861, where Mendelssohn, Mozart, Handel, and Beethoven works were performed. That left a great impression on Hubert. It also sparked the beginning of a lifelong association with the festival. That year, his brother was disgraced at Oxford for drug and alcohol use, and his sister, Lucy, died of consumption as well. Both events saddened Hubert. However, he began study at Eton College and distinguished himself at both sport and music. He also began having heart trouble, that would plague him the rest of his life. Eton was not known for its music program, and although some others had interest in music, there were no teachers there that could help Hubert much. He turned to George Elvey, organist of St George’s Chapel, Windsor Castle, and started studying with him in 1863. Hubert eventually wrote some anthems for the choir of St George’s Chapel, and eventually earned his music degree. While still at Eton, Hubert sat for the Oxford Bachelor of Music exam, the youngest person ever to have done so. His exam exercise, a cantata: “O Lord, Thou hast cast us out” astonished the Heather Professor of Music, Sir Frederick Ouseley, and was triumphantly performed and published in 1867. In 1867 he left Eton and went to Exeter College, Oxford. He did not study music there, his music concerns taking second place, but read law and modern history. However, he did go to Stuttgart, Germany, at the urging of Henry Hugh Pierson, to learn re-orchestration, leaving him much more critical of Mendelssohn’s works. When he left Exeter College, at his father’s behest, he felt obliged to try insurance work, as his father considered music only a pastime (too uncertain as a profession). He became an underwriter at Lloyd’s of London, 1870-77, but he found the work unappealing to his interests and inclinations. In 1872 he married Elizabeth Maude Herbert, and they had two daughters: Dorothea and Gwendolen. His in-laws agreed with his father that a conventional career was best, but it did not suit him. He began studying advanced piano with W S Bennett, but found it insufficient. He then took lessons with Edward Dannreuther, a wise and sympathetic teacher, who taught him of Wagner’s music. At the same time as Hubert’s compositions were coming to public notice (1875), he became a scholar of George Grove and soon an assistant editor for his new “Dictionary of Music and Musicians”. He contributed 123 articles to it. His own first work appeared in 1880. In 1883 he became professor of composition and musical history at the Royal College of Music (of which Grove was the head). In 1895 Parry succeeded Grove as head of the college, remaining in the post the remainder of his life. He also succeeded John Stainer as Heather Professor of Music at the University of Oxford (1900-1908). His academic duties were considerable and likely prevented him from composing as much as he might have. However, he was rated a very fine composer, nontheless, of orchestrations, overtures, symphonies, and other music. He only attempted one opera, deemed unsuccessful. Edward Elgar learned much of his craft from Parry’s articles in Grove’s Dictionary, and from those who studied under Parry at the Royal College, including Ralph Vaughn Williams, Gustav Holst, Frank Bridge, and John Ireland. Parry had the ability when teaching music to ascertain a student’s potential for creativity and direct it positively. In 1902 he was created a Baronet of Highnam Court in Gloucester. Parry was also an avid sailor and owned several yachts, becoming a member of the Royal Yacht Squadron in 1908, the only composer so honored. He was a Darwinian and a humanist. His daughter reiterated his liberal, non-conventional thinking. On medical advice he resigned his Oxford appointment in 1908 and produced some of his best known works. He and his wife were taken up with the ‘Suffrage Movement’ in 1916. He hated to see the WW1 ravage young potential musical talent from England and Germany. In 1918 he contracted Spanish flu during the global pandemic and died at Knightsscroft, Rustington, West Sussex. In 2015 they found 70 unpublished works of Parry’s hidden away in a family archive. It is thought some may never have been performed in public. The documents were sold at auction for a large sum. Other works he wrote include: “Studies of great composers” (1886), “The art of music” (1893), “The evolution of the art of music” (1896), “The music of the 17th century” (1902). His best known work is probably his 1909 study of “Johann Sebastian Bach”.
John Perry
C. Hubert H. Parry
George J. Elvey

1816 - 1893 Hymnal Number: 295 Composer of "DIADEMATA" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) George Job Elvey (b. Canterbury, England, 1816; d. Windlesham, Surrey, England, 1893) As a young boy, Elvey was a chorister in Canterbury Cathedral. Living and studying with his brother Stephen, he was educated at Oxford and at the Royal Academy of Music. At age nineteen Elvey became organist and master of the boys' choir at St. George Chapel, Windsor, where he remained until his retirement in 1882. He was frequently called upon to provide music for royal ceremonies such as Princess Louise's wedding in 1871 (after which he was knighted). Elvey also composed hymn tunes, anthems, oratorios, and service music.
Bert Polman
George J. Elvey
George F. Root

1820 - 1895 Person Name: George Frederick Root, 1820-1895 Hymnal Number: 325 Composer of "JEWELS" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Root, George F., MUS. DOC, born in Sheffield, Berkshire County, Mass., Aug. 30, 1820. He is much more widely known as a composer of popular music than as a hymn writer. Four of his hymns are in I. D. Sankey's Sacred Songs & Solos, 1878. Nos. 16, 100, 293, and 297. A sympathetic biographical sketch, with portrait, is in The Tonic Sol-Fa Reporter, Sep. 1886. He died Aug. 6, 1895.
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology, Appendix, Part II (1907)
=====================
George Frederick Root was born in Sheffield, Mass., August 30, 1820. His father moved to North Reading, near Boston, when the boy was six years old, and there his youth was spent.
He was always fond of music— not singing at all as a boy, but played upon every kind of instrument that came in his way. At thirteen it was his pride that he could "play a tune" on as many instruments as he was years old. His dream of life was to be a musician, although such an ambition was looked down upon by all his relatives and friends, excepting a fond mother. In the fall of 1838 he went to Boston and made an engagement to work for Mr. A. N. Johnson and take lessons on the piano.
His father and one of the brothers were at the time in South America, and the mother, with six younger children, was at home on the farm. When he secured the engagement with Mr. Johnson to receive three dollars a week and board and lessons, the neighbors became interested and encouraged him to go ahead, they promising to help look after the farm and see that the family got along. The young man's happiness over these events can better be imagined than described.
On the second day of October, 1838, he entered upon his duties in his new heaven on earth located at Harmony Hall, Mr. Johnson's music-room, in Boston. His duties were to see to the fires, care for the room, answer callers, give information about Mr. Johnson when he was out, and practice his lessons when not otherwise engaged. He worked industriously and made steady progress. It was but a few weeks till Mr. Johnson had him playing for the prayer-meeting, and but a few more till he began turning over pupils to him. In about seven weeks' time Mr. Johnson encouraged him by a considerable increase of salary. A most important event to him was meeting Dr. Lowell Mason and being accepted as a bass singer in the celebrated Bowdoin Street choir. Also, on Mr. Johnson's recommendation, he began taking private voice lessons of Mr. Geo. Jas. Webb, the then celebrated voice teacher of Boston. He continued at least a year with Mr. Webb.
His first real singing class was taught the following fall, 1839, at the North End. It lasted nearly through the winter, and on the closing night his class made him a present of a silver goblet, suitably engraved, which he kept among his treasures.
Before the first year was up Mr. Johnson proposed a five year partnership, by which Mr. Root was to receive one-third of their earnings, and the former was to have the privilege of visiting Germany part of the time if he chose. They then changed their quarters to three rooms in the basement of Park Street Church. The annual rental was six hundred dollars. They were kept quite busy.
At this time Dr. Mason's music teaching in the public schools was a growing success, and Messrs. Johnson and Root were employed to assist him. Drs. Mason and Webb had introduced what is now called Musical Conventions a year or two previous to this. They called them "The Teachers' Class." Teachers and singers were called to Boston from surrounding territory to study and practice pretty much as they do now at normals.
In 1841 Mr. Root became one of the teachers in this class. He taught vocal training and continued this work for years afterward in Dr. Mason's teachers' classes, and later incorporated the same method in his own normals. During this year Mr. Johnson went to Germany, and left the two large church choirs (Winter Street and Park Street) in charge of Mr. Root. One of the organs was played by a pupil — Mr. S. A. Bancroft.
Everything went smoothly during Mr. Johnson's absence as it did also after his return. During the last year of the five-year partnership, Mr. Root was called to take the organ at Bowdoin Street, Mr. Mason changing to Winter Street. An amicable settlement was made between Messrs. Johnson and Root, and the partnership dissolved.
In 1811, Mr. Jacob Abbott (father of Lyman Abbott)and his three brothers had established a young ladies' school in New York City. They wanted a music teacher, and offered the position to Mr. Root. They also secured him the organ and choir of the Mercer Street Church, with prospects for other good work. It required pretty strong persuasive arguments to tempt Mr. Root to leave Boston, he was doing well there, and as the sequel shows, there was an attraction in Boston that held him in too tight a grasp to be relinquished by the mere offer of greater power and place. He made up his mind, however, only after getting the consent of the powders of Boston to take with him this [to him] the greatest attraction of the city — Miss Mary Olive Woodman — an accomplished lady, a sweet singer, and a member of a prominent family of musicians. He went to New York first to prepare a home, and in August, 1845, returned for his bride, who took her place in his New York choir as leading soprano, and through his long and eventful career she was ever at his side, a true helpmeet.
He was soon employed at Rutger's Female Institute, Miss Haines' School for Young Ladies, Union Theological Seminary and the New York State Institution for the Blind. Within six weeks after he arrived in New York his time was fully occupied. He continued with Mr. Abbott's young ladies' school ten years.
While teaching in New York he continued his summer work with Messrs. Mason and Webb in Teachers' Classes. Up to the year 1849 he had written but little music; only a few hymn tunes while in Boston. He needed more music for the young ladies of his schools, so he made his first book, The Young Ladies' Choir, of which he had enough copies made for his own use, as he had no thought of offering it to the public. Then in connection with Mr. J. E. Sweetser, they compiled the Root and Sweetser's Collection.
Mr. Root did work enough for two men, hence broke down in health. Mr. Abbott suggested that he take a trip to Paris. After weighing the matter carefully, in December, 1853, he sailed, and in due time arrived at Paris, where he began studying French, voice culture and piano under celebrated teachers. After spending nearly a year abroad, he returned home in improved health and ready for active work. He began to feel the need of new music for his classes, and after some thought decided upon a musical play ; the subject and title, The Flower Queen.
At the Institution for the Blind was a young lady, a former pupil, but now a teacher who had shown some poetical talent. He asked her to help him with the words. He would suggest in prose what the flowers might say and she would put it into rhyme. She did it so well that it seldom needed any alteration. This lady was the now famous Fanny Crosby. The cantata became very popular. About this time Mr. Root wrote a half dozen simple songs for the people. They all sold pretty well, but Hazel Dell and Rosalie, the Prairie Flower, became the most popular, and had a large sale.
It was in the summer of 1853 that the first real normal was held. Mr. Root originated it, and held it in New York. The principal teachers were Messrs. Mason, Root, Hastings, and Bradbury. This school became famous. Sessions were also held at North Reading, Mass., a village near Mr. Root's "Willow Farm Home," with Dr. Mason, Mr. Webb, Mr. Bradbury and himself as principal teachers.
About this time Mr. Root decided to give up his work in New York, and devote himself entirely to conventions, normal work and authorship. He was eminently successful. Among the most eminent teachers and composers of our country have been students in Dr. Geo. F. Root's Normal Musical Institute.
In 1860 Dr. Root settled in Chicago and entered the music publishing business with his brother E. T. Root, and C. M. Cady, as "Root & Cady," Mr. Root's reputation being the most important capital of the firm. His books and popular songs soon made the new firm prosperous. Then came the war with its horror. Dr. Root wielded his musical sword in the way of writing war songs, which made him famous. The Battle Cry of Freedom, Just Before the Battle, Mother, and others, made thousands of dollars for the music house.
In the great Chicago fire of 1871 the interests of the firm of Root & Cady became engulfed in the general ruin. Their loss was upward of a quarter of a million dollars. They then sold their book catalogue, plates and copyrights to John Church & Co., of Cincinnati, and the sheet music plates and copyrights to S. Brainard's Sons, Cleveland. These sales realized about §130,000. The final result was that Dr. Root, his talented son F. W., and others became connected with John Church & Co. Under this new business relationship Mr. Root went right on with his normal and convention work; also issued a great many new books and cantatas. In 1872 the Chicago University very worthily conferred upon him the degree Doctor of Music.
In 1886 he made a trip to Scotland and England, and arranged with publishers to issue some of his cantatas. He was royally received.
Dr. Root was the author of about seventy-five books, nearly two hundred songs in sheet form, and many popular gospel songs. Dr. Root occupies a prominent place in the musical history of this country. It was Dr. Mason who lifted music from almost nothing and gave it an impetus, but he left no better follower than Dr. Root to carry on his work. He was a man of spotless integrity and high Christian character, and to know him was to love him.
At the time of Dr. Root's death he was at Bailey Island, Maine, a summer resort, where he and other relatives had cottages. On August 6, 1895, he was seized with neuralgia of the heart — and died within one hour. He was buried at North Reading, Mass., his old home.
--Hall, J. H. (c1914). Biographies of Gospel Song and Hymn Writers. New York: Fleming H. Revell Company.
George F. Root
Richard Redhead

1820 - 1901 Hymnal Number: 335 Composer of "REDHEAD 76" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Richard Redhead (b. Harrow, Middlesex, England, 1820; d. Hellingley, Sussex, England, 1901) was a chorister at Magdalen College, Oxford. At age nineteen he was invited to become organist at Margaret Chapel (later All Saints Church), London. Greatly influencing the musical tradition of the church, he remained in that position for twenty-five years as organist and an excellent trainer of the boys' choirs. Redhead and the church's rector, Frederick Oakeley, were strongly committed to the Oxford Movement, which favored the introduction of Roman elements into Anglican worship. Together they produced the first Anglican plainsong psalter, Laudes Diurnae (1843). Redhead spent the latter part of his career as organist at St. Mary Magdalene Church in Paddington (1864-1894).
Bert Polman
Richard Redhead
W. A. Ogden

1841 - 1897 Person Name: William A. Ogden, 1841-1897 Hymnal Number: 445 Composer of "BRING THEM IN" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) William Augustine Ogden USA 1841-1897. Born at Franklin County, OH, his family moved to IN when he was age six. He studied music in local singing schools at age 8, and by age 10 could read church music fairly well. Later, he could write out a melody by hearing it sung or played. He enlisted in the American Civil War in the 30th IN Volunteer Infantry. During the war he organized a male choir which became well known throughout the Army of the Cumberland. After the war, he returned home, resumed music study, and taught school. He married Jennie V Headington, and they had two children: Lowell and Marian. He worked for the Iowa Normal School, Toledo Public School System. Among his teachers: Lowell Mason, Thomas Hastings, E E Baily and B F Baker, president of the Boston Music School. He wrote many hymns, both lyrics and/or music. He later issued his first song book, “The silver song” (1870). It became quite popular, selling 500,000 copies. He went on to publish other song books. Ogden also taught music at many schools in the U S and Canada. In 1887 he became superintendent of music in the public schools of Toledo, OH. His works include: “New silver songs for Sunday school” (1872), “Crown of life” (1875), “Notes of victory” (1885), “The way of life” (1886), “Gathering jewels” (1886). He was known as a very enthusiastic person in his work and a very congenial one as well. He died at Toledo, OH.
John Perry
W. A. Ogden
W. G. Fischer

1835 - 1912 Person Name: William G. Fischer Hymnal Number: 478 Composer of "I LOVE TO TELL THE STORY" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) William Gustavus Fischer In his youth, William G. Fischer (b. Baltimore, MD, 1835; d. Philadelphia, PA, 1912) developed an interest in music while attending singing schools. His career included working in the book bindery of J. B. Lippencott Publishing Company, teaching music at Girard College, and co-owning a piano business and music store–all in Philadelphia. Fischer eventually became a popular director of music at revival meetings and choral festivals. In 1876 he conducted a thousand-voice choir at the Dwight L. Moody/Ira D. Sankey revival meeting in Philadelphia. Fischer composed some two hundred tunes for Sunday school hymns and gospel songs.
Bert Polman
W. G. Fischer
Charles C. Converse
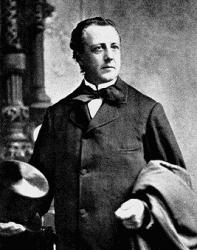
1832 - 1918 Hymnal Number: 629 Composer of "WHAT A FRIEND" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Pseudonyms: Clare, Lester Vesé, Nevers, Karl Reden, Revons
=================================
Charles Crozat Converse LLD USA 1832-1918. Born in Warren, MA, he went to Leipzig, Germany to study law and philosophy, as well as music theory and composition under Moritz Hauptmann, Friedrich Richter, and Louis Plaidy at the Leipzig Conservatory. He also met Franz Liszt and Louis Spohr. He became an author, composer, arranger and editor. He returned to the states in 1859 and graduated from the Albany, NY, Law School two years later. He married Lida Lewis. From 1875 he practiced law in Erie, PA, and also was put in charge of the Burdetta Organ Company. He composed hymn tunes and other works. He was offered a DM degree for his Psalm 126 cantata, but he declined the offer. In 1895 Rutherford College honored him with a LLD degree. He spent his last years in Highwood, NJ, where he died. He published “New method for the guitar”, “Musical bouquet”, “The 126th Psalm”, “Sweet singer”, “Church singer”, “Sayings of Sages” between 1855 and 1863. he also wrote the “Turkish battle polka” and “Rock beside the sea” ballad, and “The anthem book of the Episcopal Methodist Church”.
John Perry
Charles C. Converse
Johann Anastasius Freylinghausen

1670 - 1739 Person Name: J. A. Freylinghausen Hymnal Number: 652 Arranger of "POSEN" in Trinity Hymnal (Rev. ed.) Freylinghausen, Johann Anastasius, son of Dietrich Freylinghausen, merchant and burgomaster at Gandersheim, Brunswick, was born at Gandersheim, Dec. 2, 1670. He entered the University of Jena at Easter, 1689. Attracted by the preaching of A. H. Francke and J. J. Breithaupt, he removed to Erfurt in 1691, and at Easter, 1692, followed them to Halle. About the end of 1693 he returned to Gandersheim, and employed himself as a private tutor. In 1695 he went to Glaucha as assistant to Francke; and when Francke became pastor of St. Ulrich's, in Halle,1715, Freylinghausen became his colleague, and in the same year married his only daughter. In 1723 he became also sub-director of the Paedagogium and the Orphanage; and after Francke's death in 1727, succeeded him as pastor of St. Ulrich's and director of the Francke Institutions. Under his fostering care these Institutions attained their highest development. From a stroke of paralysis in 1728, and a second in 1730, he recovered in great measure, but a third in 1737 crippled his right side, while the last, in Nov., 1738, left him almost helpless. He died on Feb. 12, 1739, and was buried beside Francke (Koch, vi. 322-334; Allgemine Deutsche Biographie, vii. 370-71; Bode, pp. 69-70; Grote's Introduction, &c.)
Almost all Freylinghausen's hymns appeared in his own hymnbook, which was the standard collection of the Halle school, uniting the best productions of Pietism with a good representation of the older "classical" hymns. This work, which greatly influenced later collections, and was the source from which many editors drew not only the hymns of Pietism, but also the current forms of the earlier hymns (as well as the new "Halle" melodies, a number of which are ascribed to Freylinghausen himself) appeared in two parts, viz.:—
i. Geistreiches Gesang-Buch, den Kern alter und neuer Lieder...in sich haltend &c, Halle. Gedrucktund verlegt im Waysen-Hause, 1704 [Hamburg], with 683 hymns and 173 melodies. To the second edition, 1705 [Rostock University], an Appendix was added with Hymns 684-758, and 21 melodies. Editions 3-18 are practically the same so far as the hymns are concerned, save that in ed. 11, 1719 [Berlin], and later issues, four hymns, written by J. J. Rambach at Freylinghausen's request, replaced four of those in eds. 1-10.
ii. Neues Geistreiches Gesangbuch,&c, Halle . . . 1714 [Berlin], with 815 hymns and 154 melodies. In the 2nd edition, 1719 [Rostock University], Hymns 816-818, with one melody, were added.
In 1741 these two parts were combined by G. A. Francke, seven hymns being added, all but one taken from the first edition, 1718, of the so-called Auszug, which was compiled for congregational use mainly from the original two parts: and this reached a second, and last, edition in 1771. So far as the melodies are concerned, the edition of 1771 is the most complete, containing some 600 to 1582 hymns. (Further details of these editions in the Blätter für Hymnologie, 1883, pp. 44-46, 106-109; 1885, pp. 13-14.) A little volume of notes on the hymns and hymnwriters of the 1771 edition, compiled by J. H. Grischow and completed by J. G. Kirchner, and occasionally referred to in these pages, appeared as Kurzgefasste Nachricht von ältern und ncuern Liederverfassern at Halle, 1771.
As a hymnwriter Freylinghausen ranks not only as the best of the Pietistic school, but as the first among his contemporaries. His finest productions are distinguished by a sound and robust piety, warmth of feeling depth of Christian experience, scripturalness, clearness and variety of style, which gained for them wide acceptance, and have kept them still in popular use. A complete edition of his 44 hymns, with a biographical introduction by Ludwig Grote, appeared as his Geistliche Lieder, at Halle, 1855. A number of them, including No. v., are said to have been written during severe attacks of toothache. Two (“Auf, auf, weil der Tag erschienen"; "Der Tag ist hin") are noted under their own first lines.
i. Hymns in English common use: --
i. Monarche aller Ding. God's Majesty. 1714, as above, No. 139, in 11 stanzas of 6 lines, repeated in Grote, 1855, p. 88, and as No. 38 in the Berlin Geistliche Lieder, ed. 1863. A fine hymn of Praise, on the majesty and love of God. Translated as:—
Monarch of all, with lowly fear, by J. Wesley, in Hymns & Sacred Poems, 1739 (P. Works, 1868-1872, vol. i. p. 104), in 8 stanzas of 4 lines, from st. i., ii., v.-vii., ix.-xi. Repeated in full in the Moravian Hymnbook, 1754, pt. i., No. 456 (1886, No. 176); and in J. A. Latrobe's Collection, 1841. The following forms of this translation are also in common use:--
(1) To Thee, 0 Lord, with humble fear, being Wesley's st. i., iii.-v., vii., viii. altered as No. 156 in Dr. Martineau's Hymns for Christian Church & Home, 1840, and repeated in Miss Courtauld's Psalms, Hymns & Anthems, 1860, and in America in the Cheshire Association Unitarian Collection, 1844.
(2) Thou, Lord, of all the parent art, Wesley's, st. iii.-v., vii. altered in the College Hymnal, N. Y., 1876.
(3) Thou, Lord, art Light; Thy native ray, Wesley's st. iv., v., vii., in Hymns of the Spirit, 1864.
ii. 0 reines Wesen, lautre Quelle. Penitence. Founded on Psalm li. 12, 1714, as above, No. 321, in 7 stanzas of 8 lines, repeated in Grote, 1855, p. 41, and in Bunsen's Versuch, 1833, No. 777 (ed. 1881, No. 435). The only translation in common use is:—
Pure Essence: Spotless Fount of Light. A good and full translation by Miss Winkworth in the first series of her Lyra Germanica, 1855, p. 43, and in her Chorale Book for England, 1863, No. 113.
iii. Wer ist wohl wie du. Names and offices of Christ. One of his noblest and most beautiful hymns, a mirror of his inner life, and one of the finest of the German "Jesus Hymns." 1704, as above, No. 66, in 14 st. of 6 l., repeated in Grote, 1855, p. 33, and is No. 96 in the Berlin Geistliche Lieder, ed. 1863. The translations in common use are:
1. 0 Jesu, source of calm repose, by J. Wesley, being a free translation of st. i., iii., v., viii., xiii. First published in his Psalms & Hymns, Charlestown, 1737 (Poetical Works, 1868-1872, vol. i. p. 161). Repeated in full as No. 462 in pt. i. of the Moravian Hymnbook, 1754. In the 1826 and later editions (1886, No. 233) it begins, "Jesus, Thou source." The original form was included as No. 49 in the Wesley Hymns & Spiritual Songs , 1753, and, as No. 343, in the Wesley Hymnbook, 1780 (1875, No. 353). Varying centos under the original first line are found in Mercer's Church Psalter & Hymn Book, 1855-1864; Kennedy , 1863; Irish Church Hymnal, 1869-1873; J. L. Porter's Collection, 1876, &c. It has also furnished the following centos:—
(1) Messiah! Lord! rejoicing still, being Wesley's st. iv.-vi. altered in Dr. Martineau's Collection of Hymns for Christian Worship, 1840.
(2) Lord over all, sent to fulfil, Wesley's st. iv., iii., v., vi. in the American Methodist Episcopal Hymnbook, 1849.
2. Who is like Thee, Who? a translation of st. i., ii., v., vii., x., xiii., as No. 687, in pt. i. of the Moravian Hymnbook, 1754. Translations of st. xi., xiv. were added in 1789, and the first line altered in 1801(1886, No. 234), to "Jesus, who with Thee." The translations of st. i., ii., x., xiv., from the 1801, altered and beginning, "Jesus, who can be," are included in America in the Dutch Reformed Hymns of the Church, 1869; Hymns & Songs of Praise, N. Y., 1874; and Richards's Collection, N.Y., 1881.
3. Who is there like Thee, a good translation of st. i., ii., viii., xiv., by J. S. Stallybrass, as No. 234 in Curwen's Sabbath Hymnbook, 1859, repeated in the Irish Church Hymnal, 1873, and in W. F. Stevenson's Hymns for Church & Home, 1873.
4. Who is, Jesus blest, a translation of stanzas i., ii., v., vi., xii., xiv., by M. Loy, in the Ohio Lutheran Hymnal, 1880.
5. Who, as Thou, makes blest, a good translation, omitting st. vii., ix., x., contributed by Dr. F. W Gotch to the Baptist Magazine, 1857. Repeated in the 1880 Supplement to the Baptist Psalms & Hymns, 1858.
The translations not in common use are: —
(1) "Whither shall we flee," by Miss Dunn, 1857, p. 55. (2) "Who has worth like Thine," in the U. P. Juvenile Miss. Magazine, 1857, p. 217. (3) "Thou art First and Best," by Miss Winkworth, 1869, p. 267.
ii. Hymns translated into English but not in common use:—
iv. Herr und Gott der Tag und Nächte. Evening. 1705, as above, No. 755, in 6 stanzas, Grote, p. 105. Translated by H. J. Buckoll, 1842, p. 106, beginning with stanza. ii.
v. Mein Herz, gieb dioh rufrieden. Cross and Consolation. First in the Halle Stadt Gesangbuch, 1711, No. 503, in 11 stanzas; repeated 1714, No. 450, and in Grote, p. 71. Translated by Dr. G. Walker, 1860, p. 86.
vi. 0 Lamm, das keine Sünde je beflecket. Passiontide. 1714, No. 85, in 19 stanzas, Grote, p. 14. Translated as, (1) "Lamb, for Thy boundless love I praises offer," of st. xii. as stanza i. of No. 1023 in the Supplement of 1808 to the Moravian Hymn Book, 1801 (1849, No. 121). (2) "O Lamb, whom never spot of sin defiled," in the British Magazine, June, 1838, p. 625.
vii. 0 Lamm, das meine Sündenlast getragen. Easter Eve. 1714, No. 95, in 8 stanzas; Grote, p. 23. Translated as "Christ Jesus is that precious grain," a translation of st. v. by F. W. Foster, as No. 71 in the Moravian Hymnbook, 1789 (1886, No. 921).
viii. Zu dir, Herr Jesu, komme ich. Penitence. Founded on St. Matthew xi. 28-30. 1714, as above, No. 306, in 4 stanzas; Grote, p. 39. Translated by Dr. H. Mills, 1845 (1856, p. 80). [Rev. James Mearns, M.A.]
--John Julian, Dictionary of Hymnology (1907)
Johann Anastasius Freylinghausen

 My Starred Hymns
My Starred Hymns


